Windows 11, the latest operating system from Microsoft, brings several significant changes and improvements compared to its predecessor, Windows 10. In this article, we will explore the differences between the two versions of Windows, focusing on various aspects of the user interface and functionality.
System Requirements
Windows 11 initially had strict CPU requirements, but Microsoft later revised them. The controversial requirement of TPM 2.0 and secure boot raised concerns among users, although it can be bypassed for fresh installations. Windows 11 requires a larger storage space (64 GB) compared to Windows 10 (20 GB), but with updates, Windows 10 occupies more space. RAM requirement increased to 4 GB, but Windows 11 uses less RAM overall.
Performance
Windows 11 offers slight performance improvements over Windows 10. It features better hardware scheduling, optimized support for chiplet and hybrid architectures, and improved memory management. These enhancements result in more efficient processing and better gaming performance.
Gaming Enhancements
Windows 11 brings several quality of life improvements for gamers. It incorporates features from Xbox Series X, such as Auto HDR, which enhances games that don’t support HDR natively. Windows 11 offers better latency and variable refresh rate technology, and it has improved compatibility with G-Sync and borderless windowed modes. The new OS also includes better voice support and enhanced HDR functionality.
User Interface Changes
Windows 11 features a centered taskbar and a redesigned Start menu compared to the left-aligned taskbar in Windows 10. The new OS provides improved multitasking with various snap layouts, including a three-window split and five-window grid. Dark mode is available system-wide, but an automatic switch based on time would have been a welcomed addition.
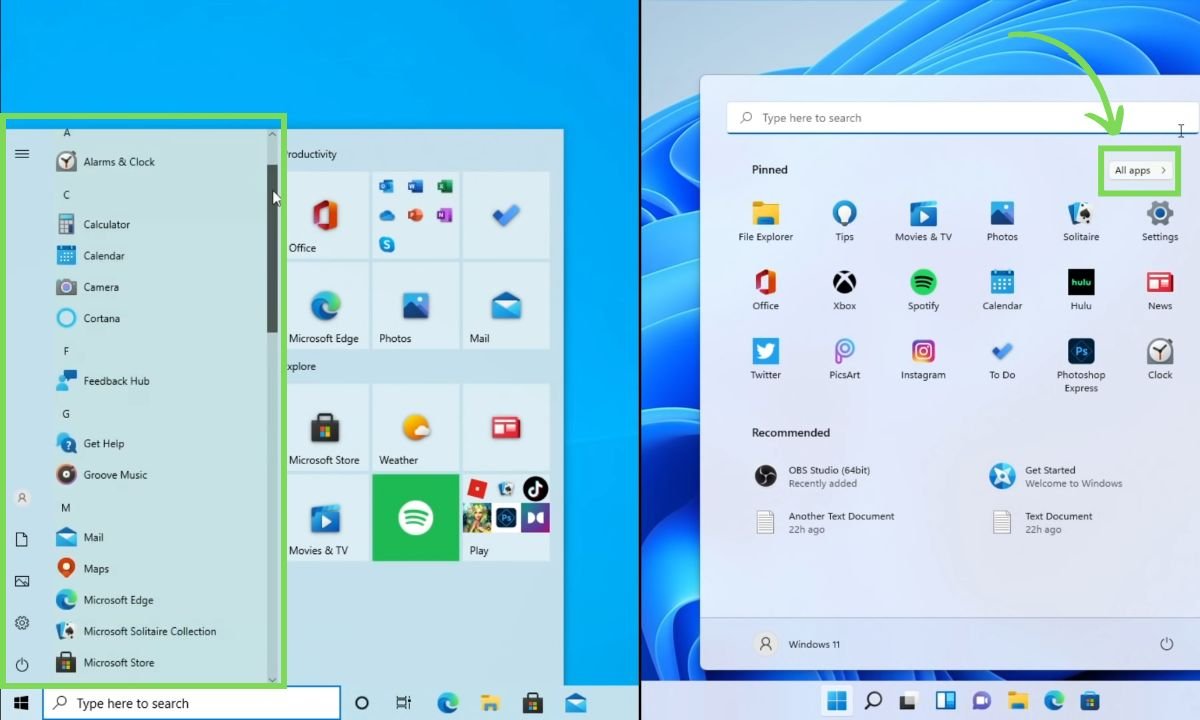
Windows 11 vs. Windows 10: Differences
Start Menu Redesign
One of the most noticeable changes in Windows 11 is the complete redesign of the Start Menu. In Windows 10, pinned apps were located on the right side, while in Windows 11, they are moved to the top half. Live tiles have been replaced with static icons in a grid format.

The search bar is now integrated into the Start Menu itself, and the side panel shortcuts have been moved to the bottom.
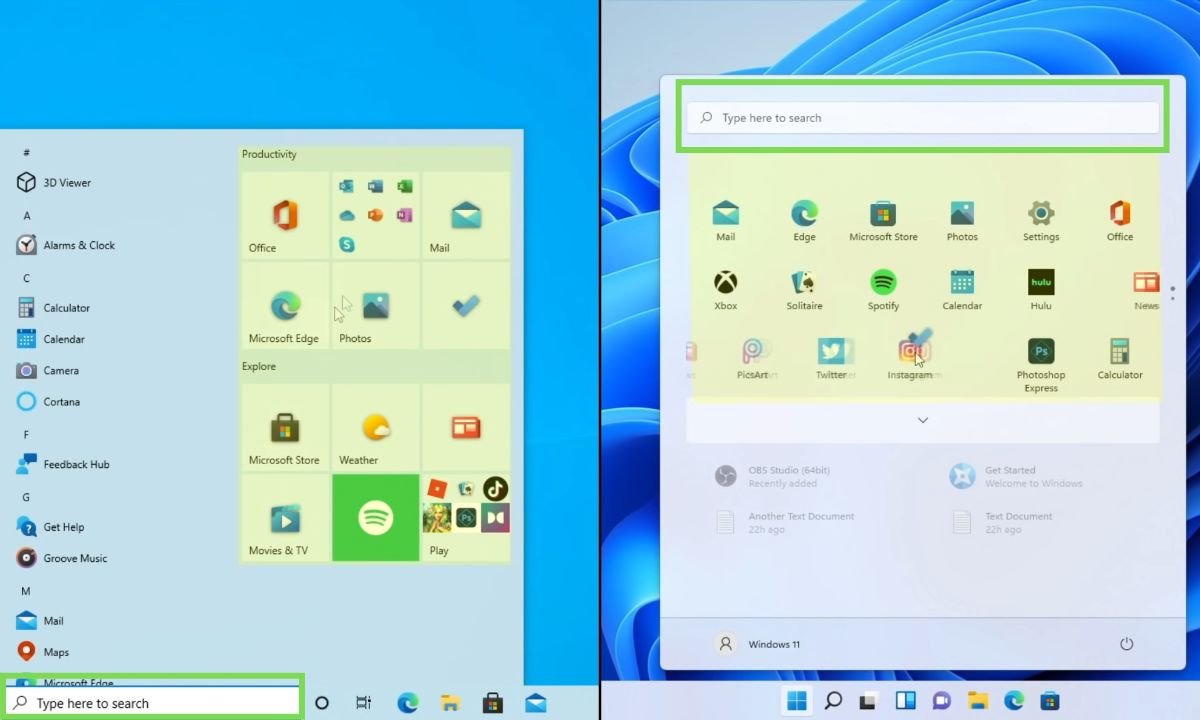
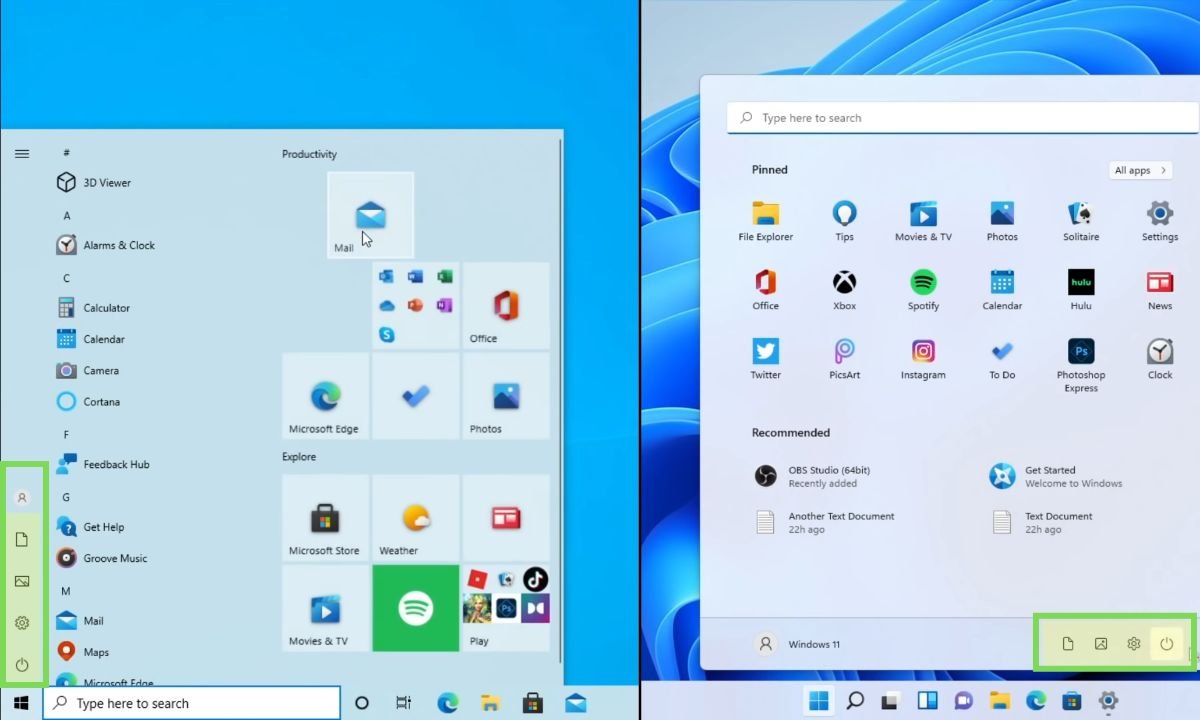
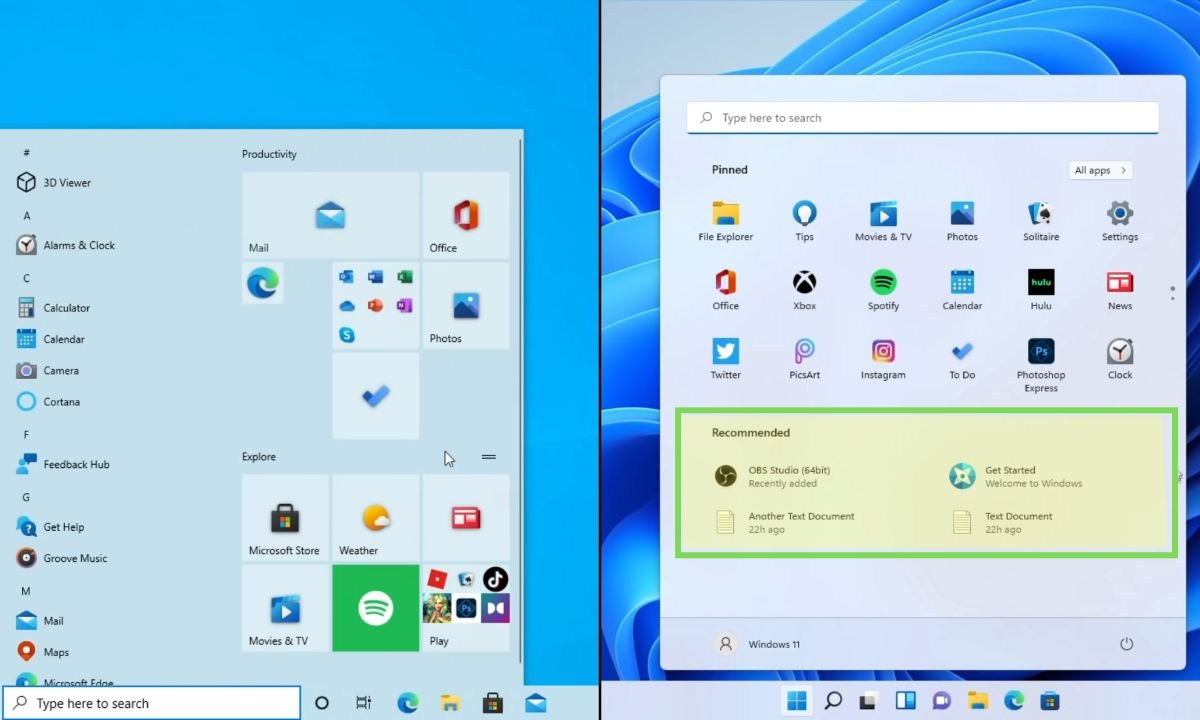
Additionally, Windows 11 introduces a new “Recommended” section that displays recently used programs and files, synced with OneDrive.
Taskbar Changes
The taskbar in Windows 11 also undergoes several changes compared to Windows 10.
Icons on the taskbar are now centered by default, although there is an option to revert to left alignment.
The UI for active and idle programs is now indicated by a color and length of a line in the taskbar icon. Taskbar animations have been redesigned, including new animations for downloading, installing, and user account control prompts.

The taskbar size options and the ability to drag and drop files have been removed in Windows 11, which is a notable difference from Windows 10.
UI Design and Visual Updates
Windows 11 introduces a new visual design with rounded corners, which is consistent throughout the operating system.

The majority of icons in Windows 11 have been redesigned to align with the modern design language. The default wallpaper has also been updated, featuring a blue bloom.

Light mode becomes the default theme in Windows 11, replacing the hybrid dark taskbar and light apps of Windows 10. The Windows logo itself has undergone a redesign, resembling the Microsoft logo more closely.

System Sounds and Visual Effects
Windows 11 offers different sounds for its dark and light modes, providing distinct audio experiences. The spinning logo when signing in or out, updating, or restarting now shows a black background consistently, unlike Windows 10, which rotated the accent color. Additionally, app splash screens in Windows 11 display a black or white background, while Windows 10 used the accent color of the background.
Action Center and Notifications
The Action Center in Windows 10 has been reorganized in Windows 11. It is separated into two menus: Quick Settings and Notifications.
Quick Settings replaces the toggles found at the bottom of the Action Center in Windows 10 and now includes controls for volume, brightness, and Wi-Fi.
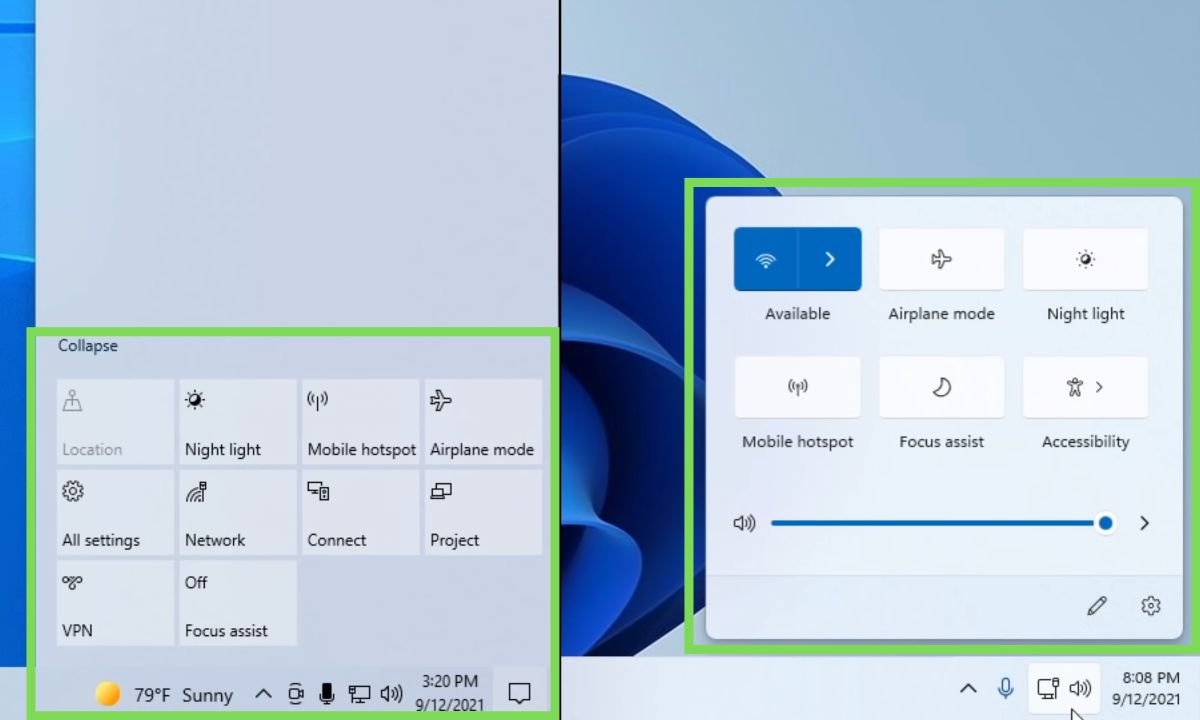
Notifications in Windows 11 are no longer inside a bar but are located above the calendar. The new notifications are round and offer a shortcut to focus settings in the Settings app. The calendar itself has minimal changes, with centered elements and the removal of the detailed clock.

Snap Assistant and Multitasking
Windows 11 introduces several improvements to Snap Assistant and multitasking features. The Task Viewer in Windows 11 has been simplified, and the timeline feature from Windows 10 has been removed.
Windows 11 allows for different wallpapers on each virtual desktop, unlike Windows 10, which had a single wallpaper for all virtual desktops.

The snap and resize animations have been changed in Windows 11, offering a more fluid experience. Windows 11 also introduces window grouping in the taskbar, which allows users to preview and open groups of apps more easily.
Built-in Apps and Programs
Several built-in applications and programs have been updated in Windows 11. The File Explorer features various UI changes, including a simplified ribbon UI and less space-consuming icons.

The Settings App undergoes a complete redesign, making it more organized, easier to navigate, and visually appealing with enlarged icons, pictures, and new animations.

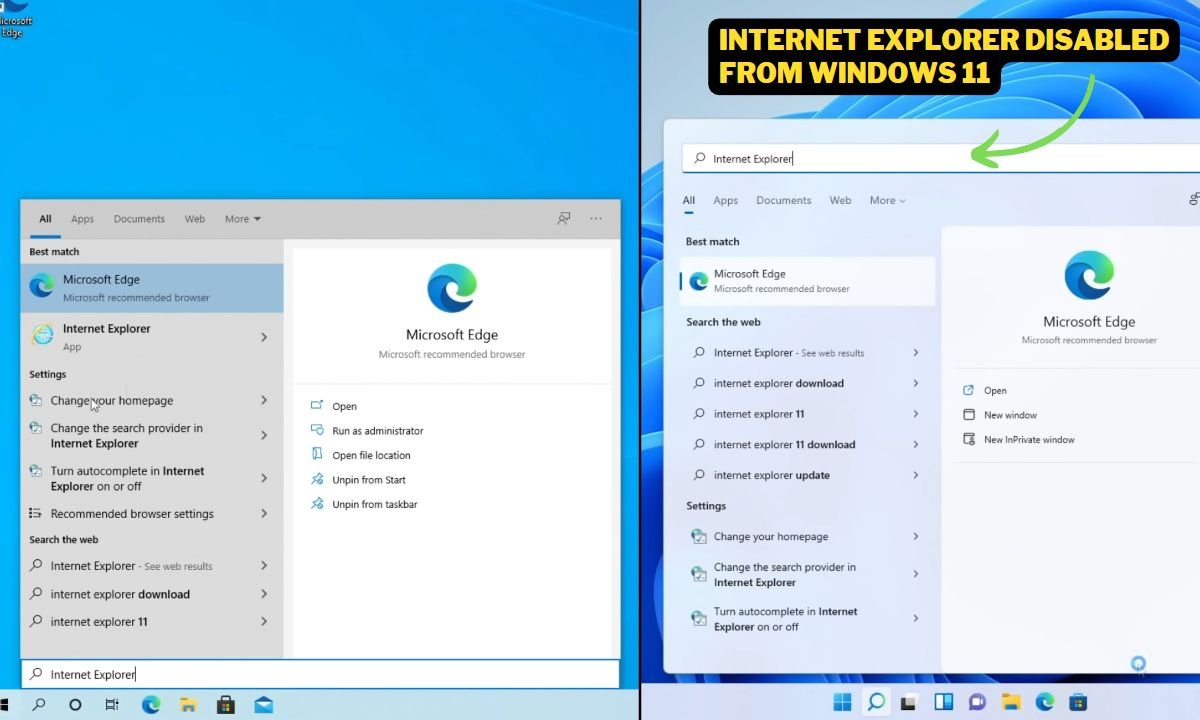
Internet Explorer finally disabled from windows 11.
Windows 11 also consolidates and updates several Windows accessories, eliminating duplicate versions. For example, Snip & Sketch is replaced by an updated Snipping Tool with a modern UI and enhanced features.

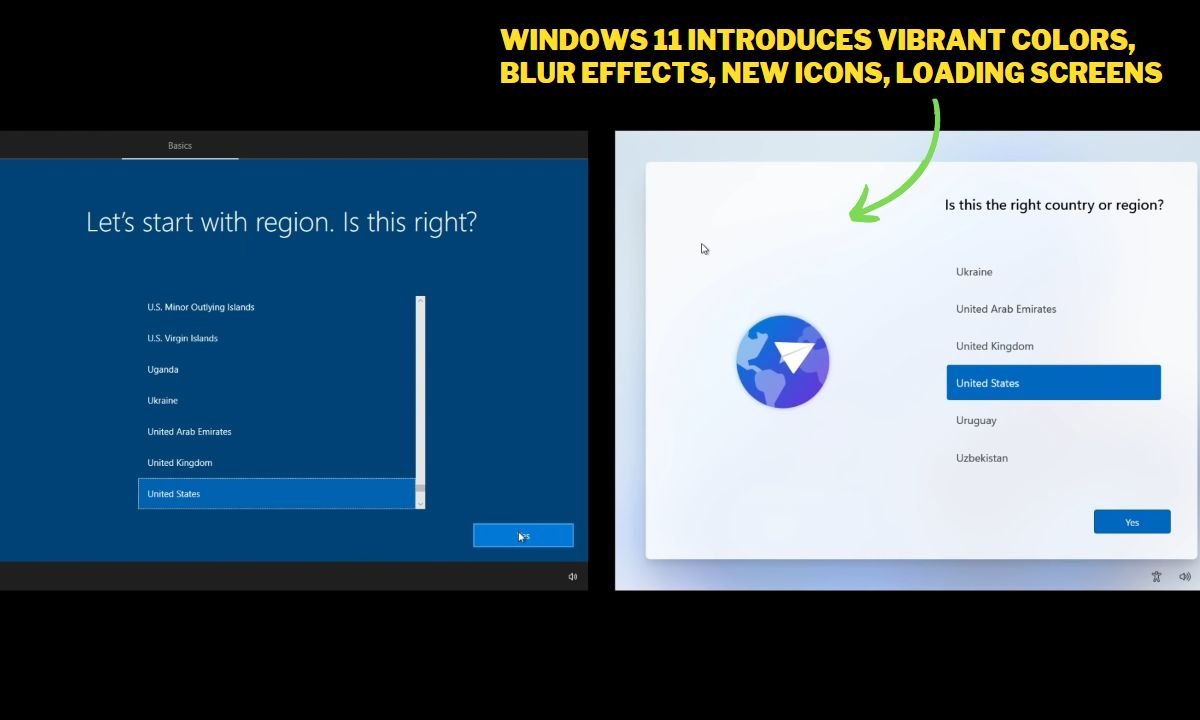
Setup Experience
The setup experience in Windows 11 undergoes a complete redesign, offering a fresh look and improved animations compared to Windows 10.
Windows 11 introduces vibrant colors, new icons, loading screens, and other enhancements to create a visually appealing setup process. Cortana, which played a significant role in the Windows 10 setup experience, is no longer a part of the Windows 11 setup.
Windows Updates
Windows 11 introduces changes to Windows Update, offering a more user-friendly and informative experience compared to Windows 10. During restarts, Windows 11 displays updated text using natural language to describe the update progress, providing clearer information to users.

Windows Update in Windows 11 also includes estimated time remaining for completing updates, which is a new addition not present in Windows 10.
Conclusion!
Windows 11 brings numerous improvements and enhancements over its predecessor, Windows 10. The built-in programs and apps receive updates, providing a more streamlined and visually appealing experience. Tablet features and touch controls are refined to optimize usability on touch-enabled devices. The setup experience undergoes a complete redesign, introducing vibrant colors, new icons, and improved animations. Additionally, Windows Update in Windows 11 offers clearer information and estimated completion times, while the frequency of feature updates is adjusted to an annual cycle.
Ultimately, the decision to upgrade to Windows 11 depends on individual preferences, needs, and device compatibility.




